Do you want to know the differences between Web Hosting and Domain Name?
You’ll get your answers here: Web Hosting vs Domain.
Web hosting and domain names are the two pillars where your website stands.
Both are entirely different terms. They have different meanings and specific functions on your website. So, you should know about them if you want to keep yourself aware.
These two big words: domain and hosting are talked together a lot.
But, many people don’t know the difference between them. You might not too! Of course, it’s hard to tell, especially if you’re a beginner.
So, we’re here to help you easily understand the domain, hosting, their differences, relation, and how to get them for your site.
Let’s start with the basic differences between them.
Quick Comparison Table: Web Hosting vs Domain Name
Are you short of time?
You can check out the table below to quickly understand the difference between Web Hosting and Domain Name.
This comparison will help you see how they work together but serve different purposes.
| Feature | Web Hosting | Domain Name |
| Definition | A service that stores website files and makes them accessible online. | A unique address (URL) that directs users to a website. |
| Purpose | Provides storage space, bandwidth, and server management for websites. | Acts as an identifier for a website so users can easily find it. |
| How It Works? | Hosts website files, databases, and content. | Maps a domain name to the hosting server via DNS. |
| Key Components | Server, storage, security, uptime, support. | Domain extensions (.com, .org, .net), WHOIS privacy, DNS settings. |
| Can You Have One Without the Other? | No, web hosting is needed to store website content. | No, without a domain, users won’t have a way to access the site. |
| Who Provides It? | Hosting companies like Hostinger, Bluehost, Kinsta, and more. | Domain registrars like Namecheap, GoDaddy, and so forth. |
| Cost Range | Starts from $1.99–$30/month and more (varies by type of hosting). | Starts from $6.49–$50/year (premium domains cost more). |
| What Happens If You Don’t Renew? | Your website goes offline until you renew or move to another host. | Your domain becomes available for others to purchase. |
| Do You Need Both? | Yes, for a fully functional website. | Yes, unless you’re using a subdomain (e.g., example.wordpress.com). |
A. Web Hosting vs. Domain Name: Explained
Simply, Web hosting is a place to store your website on the internet. It’s the space where your entire website files including code, media, images, and database reside physically.
Web hosting services are provided by businesses commonly called hosting companies. They do the job of storing your website, keeping it safe, and making it available to internet users worldwide. They store the files on special powerful computers called servers.

Now, a domain name is a unique name that internet users use to access your website. It’s the address that helps to locate your website on the internet. Whenever people enter your domain name into their web browser, it shows them your website.
A domain name can’t just be a random name. Rather, it should be unique and distinguishing. In fact, no two websites can have the same domain name. Having that, every domain name comes to have a unique identity.
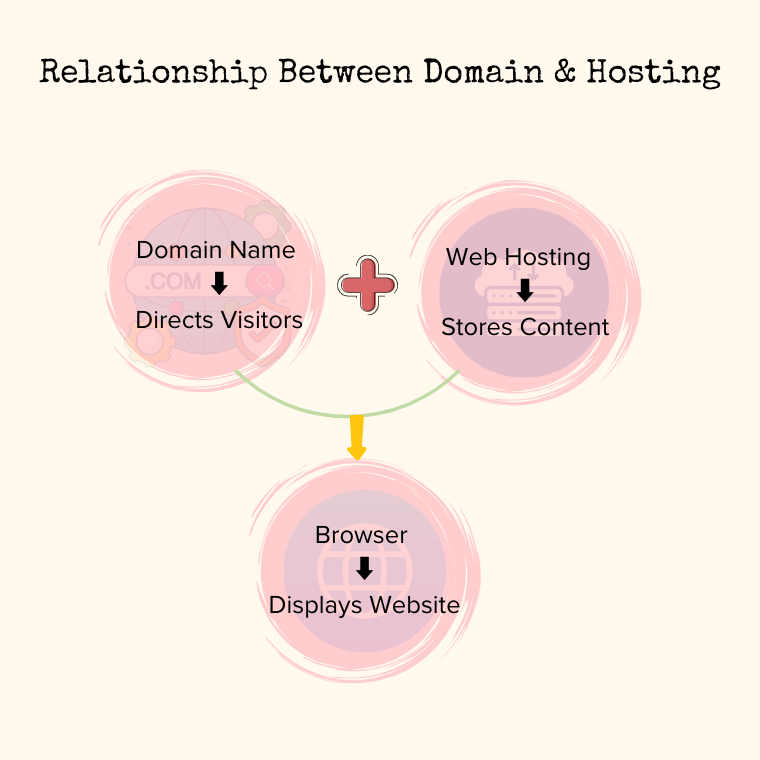
How are Domain Name and Web Hosting Related?
By now, you probably understand that domain names and web hosting are two separate things. But when it comes to building a website, they go hand in hand.
So, what’s the connection between them?
Think of it this way:
If your website were a house, web hosting would be the land where it’s built, and your domain name would be the address that helps people find it.
Without hosting, there’s no space to store your website’s content. Without a domain name, no one would be able to locate your site on the internet.To create a website, you need both a domain name and hosting, which can be purchased separately from different providers.
Domain registrars like Namecheap and GoDaddy sell domain names, while hosting companies like Hostinger, Bluehost, Cloudways, etc provide web hosting.
However, some companies offer both domain and hosting as a package, making it easier for beginners to set up their websites.
Once you have hosting, your website files (such as text, images, and code) are stored on a server. The domain name then acts as a shortcut, directing users to that server whenever they enter your website address in their browser.
Without a domain name, visitors would have to remember a complex IP address to access your site—something no one wants to do!
In short, hosting is where your website lives, and the domain name is how people find it. Together, they make your website accessible to the world.
B. What is a Domain Name? – Understanding More!

Like we’ve already explained, a domain name (or domain) is the unique name of your website. It’s what people type in their browsers if they have to visit your site. So, it’s also referred to as the address of your website or the web address.
For example: ‘SiteNerdy.com‘ is the domain name of our website.

Similarly, Google.com, Wikipedia.org, Facebook.com, etc. also are the popular domain names of respective sites.
Now, let’s understand an easy concept of why domain names came into practice.
Actually, websites are identified on the web by IP addresses of the servers they are stored in. An IP address is the combination of numbers separated by dots. It looks like this:
216.58.214.4
Want to see for yourself? Just enter the above number in your web browser’s address bar. You’ll see our favorite search engine Google opening. Isn’t that cool?
Likewise, the IP address of the server gives the location of every respective website.
Computers indeed identify these kinds of numbers and locate the relevant websites. But for people, it’s very hard to catch on. You’re not supposed to remember the IP address of every website that you want to visit.
That’s where domain names came in. The idea is just to use a simple word(s) rather than lengthy numbers to identify and locate websites.
For example, typing ‘Google.com’ instead of ‘216.58.214.4’ to visit Google is so much easier.
Domain Name Structure
Breaking down a domain name, it consists typically of 2 parts. Namely:
- Second-Level Domain (Registered Domain)
- Top-Level Domain (Domain Extension)
If you feel we’re getting techie on you with these terms, don’t worry! We’ll make it as easy as ABC.
Let’s take our site’s domain name for an example.
SiteNerdy.com
It consists of 2 parts. The first one is ‘SiteNerdy’, which is the second-level domain. It’s followed by ‘com’, a top-level domain. The Period ‘.’ is a separator between the two.
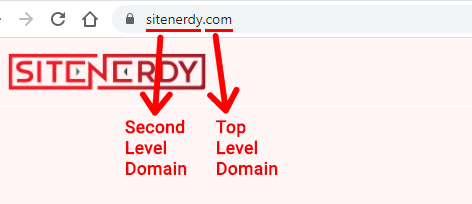
So simply, you can say the second level domain is the name of your website, business, organization, or brand.
Now, how do you get the domain name for your website?
Well, you get to register your custom domain name like ours from domain name registrars like GoDaddy, Namecheap, Domain.com, Shopify, etc. That’s why; a second-level domain is also called the registered domain.
Having said that, you can’t register the second level domain name if it’s already taken.
Domain name registration is a paid service i.e. you have to purchase it. However, some website builders like WordPress.com, Wix, etc. provide a sub-domain for free. The bottom line, you’ll have to build a website using their platform.
The top-level domain name is the extension part of your domain name. These extensions normally describe what your website’s purpose is.
For example:
- .com: Commonly used by commercial or business websites
- .net: Used by Networking companies
- .edu: Educational establishments use this extension.
- .org: Used by non-commercial websites
You get to choose the top-level domain during the domain registration. We recommend choosing ‘.com’ for your site as it’s the most popular extension.
Domain Name Registration
It’s the process of registering an available domain name for your website. It’s mostly a paid service, however, you can get free domains as well. But, keep in mind that only a certain category of domain names are free.
The companies that allow you to register domain names are called domain registrars. They let you search domain name availability, choose extensions, and inquire about their prices. Also, a registrar should allow transferring your domain name to a different registrar.
Buying a domain name includes picking a second-level domain and a top-level domain as well. The cost of registration depends hugely on the top-level domains you choose.
Before registering the domain, you need to find a suitable domain name. You can find the best domain name with the help of domain name generators.
Now, make yourself clear with a fact. You can’t get any domain name for a lifetime. You can only own the domain name only for a certain period. So, after the validity time expires, you’ll have to renew the registration if you want to continue using it.
Let me share an interesting incident. You might have heard how the internet giant Google lost its domain name. It looked like Google forgot to renew their domain name ownership and somebody else registered it. Luckily, they could recover it within a minute.
So, it’s clear that the internet treats everybody equally. Even Google’s domain name is not permanent with them and could lose if not renewed the registration.
While registering the domain name, consider the following things.
- The domain name should be catchy.
- It should be short in length.
- Prefer .com domain.
- Avoid hyphens and doubled letters.
- Add relevant keywords.
C. What is Web Hosting? – Understanding More!
As already talked, web hosting is the service that allows you to keep your website files on remotely located computers (servers). Website files normally include codes (HTML, CSS, PHP, etc), images, texts, videos, animation, etc.

The hosts also provide internet connections so that your site becomes live. In other words, having a web hosting service gets your website online accessible by your visitors.
Similar to domain names, you’ll have to buy the hosting service. Purchasing the service is like renting space for storing and showcasing your website. Moreover, the cost depends on the volume of server resources you use in your site. And, the resources you need depends on the type of your website, the number of visitors, website size, etc.
However, you can also get free hosting if you want. There are tons of these out there. But, they are low on storage, bandwidth, and speed. Also, they don’t guarantee the security and backup of your data. So, don’t get attracted to free hosting if you’re into serious business with your website.
You can get reliable paid hosting for your online presence from tons of providers available. To name a few, DreamHost, Bluehost, HostGator, SiteGround, InMotion Hosting, etc. are some of the best web hosting companies.
The Working of Web Hosting
Web hosting companies own tons of powerful computers called servers. The servers are kept in a highly secure and stable environment to run without any failure and stoppage. Having that, your site is live 24/7 i.e. accessible at any time.
When you buy a hosting service, actually you’re renting the server’s storage and network connection (bandwidth).
To manage your site’s web hosting, you’ll have to sign up and create a hosting account with a hosting company you like. Then, you’ll be provided a hosting control panel. From there, you can upload website files, set up databases, install website builders, install an SSL certificate, etc.
Most importantly, you’ll have to enter your domain name into your hosting account. Having that, the domain name points to your website in the server whenever people enter it in the web browser.
Now, the Domain Name System (DNS) is the one finding your website from the given domain name. It’s the system that converts domain names into equivalent IP addresses, searches it in web directories, locates the server, and supplies the website data to the web browser.
Types of Web Hosting
Different website niches like blogs, small businesses, entertainment, eCommerce, etc. have different requirements. So, hosting companies provide different models to best meet the requirement of every type of website.
Some of the types of web hosting are:
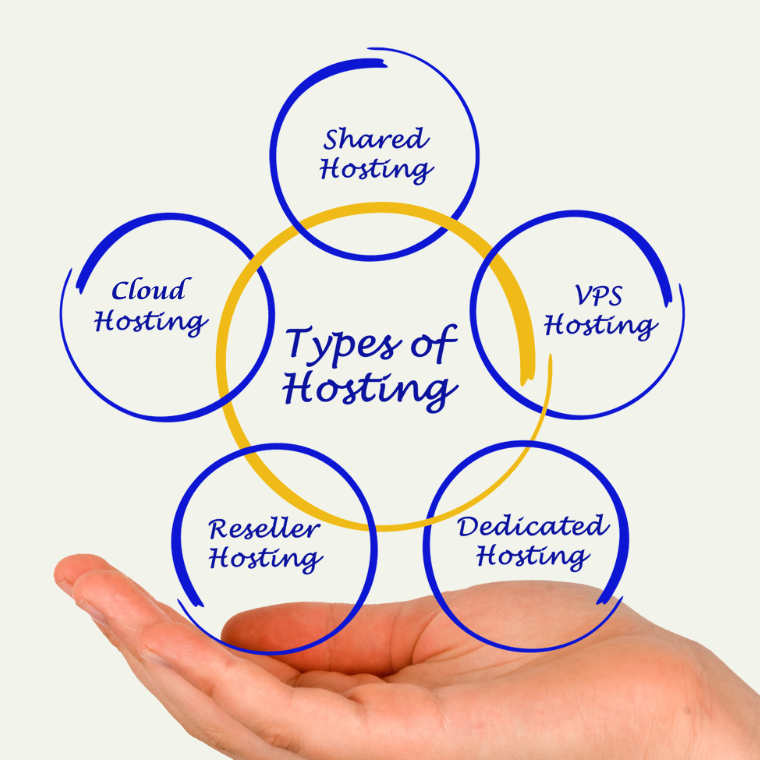
1. Shared Hosting:
Shared hosting is the type of hosting in which multiple websites use a single server. Then, the websites share CPU, memory, bandwidth, and RAM provided by that server.
By sharing the resources the websites split the cost among them. This makes shared hosting the most affordable.

This type of hosting is applicable for starter websites with a low expectation of traffic. Static websites, blogs, small businesses, etc. can use shared hosting to host their site.
2. VPS Hosting:
Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a special type of hosting. Your website on VPS hosting will share the server with other websites. However, it will have a dedicated resource allocation inside the server.
In other words, VPS hosting is a dedicated hosting inside of a shared hosting server. Multiple websites use the same server as in shared hosting. But, the resources are partitioned and reserved for your site as in dedicated hosting.
Also, this kind of hosting is moderately costly and good for medium-sized businesses with growing traffic.
3. Dedicated Hosting:
This type of hosting dedicates a whole server for a single website. Thus, if you have a dedicated server, then you can configure your website according to your needs. The server will manage the resources to fulfill your specifications.

This type of hosting provides professional support and security to websites. It’s the most expensive type of hosting and applicable to large businesses and enterprise websites.
4. Reseller Hosting:
Reseller hosting allows individuals or businesses to buy hosting in bulk from a provider and resell it as their own service.
It includes a control panel, white-label branding, and automated billing tools. This makes it ideal for agencies, developers, and entrepreneurs who want to offer hosting without managing servers.
The main server is owned by the hosting provider, but resellers manage their own customers, pricing, and support. It’s a cost-effective way to start a hosting business without large infrastructure investments.
5. Cloud Hosting:
Cloud is the newly introduced hosting system on the web. In this type of hosting, many servers work together and combine bits of multiple resources. And, it allows websites to use resources as per their needs.

It’s useful for websites that require a dynamic change in requirements. If you use cloud hosting, Then you don’t have to change your hosting to a different plan. Rather, you can just extend the resource as you need.
For example, if your server storage is full and you want to have more, then you can simply allocate additional space to your site.
Hence, cloud hosting has scalable (easily increased and decreased) resources and a pay-per-use model.
D. Buying Domain and Hosting
When setting up a website, you can either buy a domain and hosting separately (from different providers) or purchase them together from a single provider.
There are many providers for domain names and web hosting, but we prefer Namecheap for domains and Hostinger for hosting when buying separately.
If you want an easier setup, Hostinger and Bluehost offer both in one package.
Here’s how you can do it.
i) How to Buy Domain & Hosting Separately?
If you prefer to register your domain with Namecheap and host your website with Hostinger, follow these steps:
Step 1: Buy a Domain from Namecheap
First of all, go to the official Namecheap website and search for your preferred domain name.
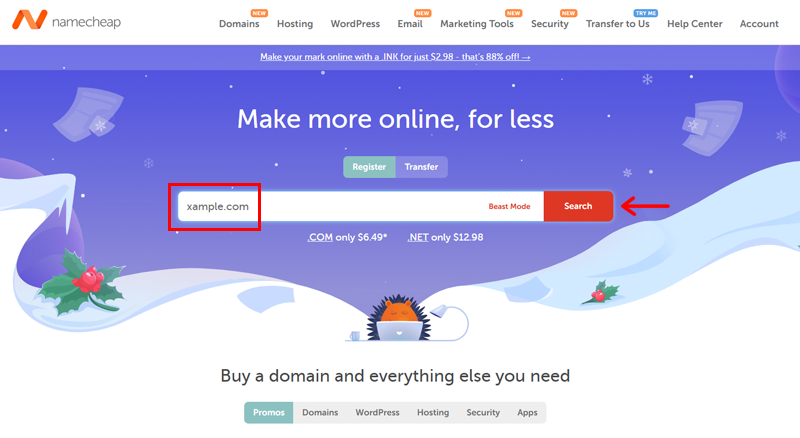
If you’ve not come up with a name, then you can also use its ‘Beast mode’ to search for one.
Once you find an available option, click on the ‘Add to Cart’.
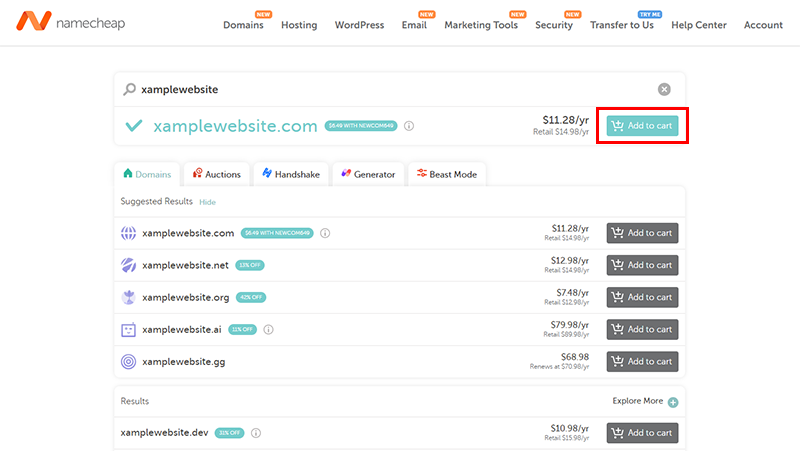
Then click on the ‘Confirm Order’ option, also if you’ve got any Promo Code then also you can apply for it.
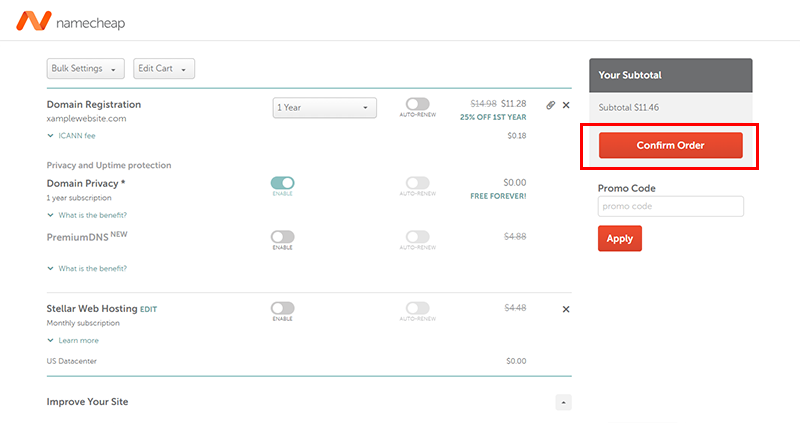
Next, you can create an account or log in, choose a payment method (Credit Card, PayPal, etc.), and complete the purchase.
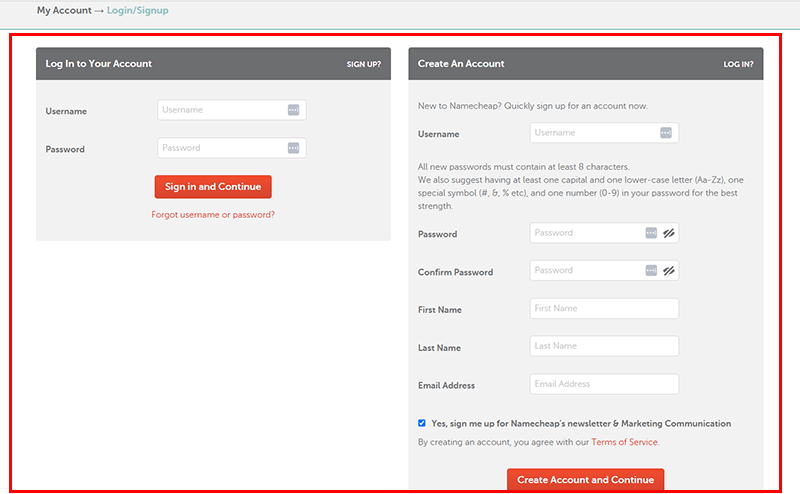
After payment, you need to go to Dashboard > Domain List to access your domain. For more guidance, you can check its article on registering a domain name and domain management.
Step 2: Buy Hosting from Hostinger
Next, if you’re will to buy the hosting separately, then go to Hostinger and select a hosting plan that suits your needs.
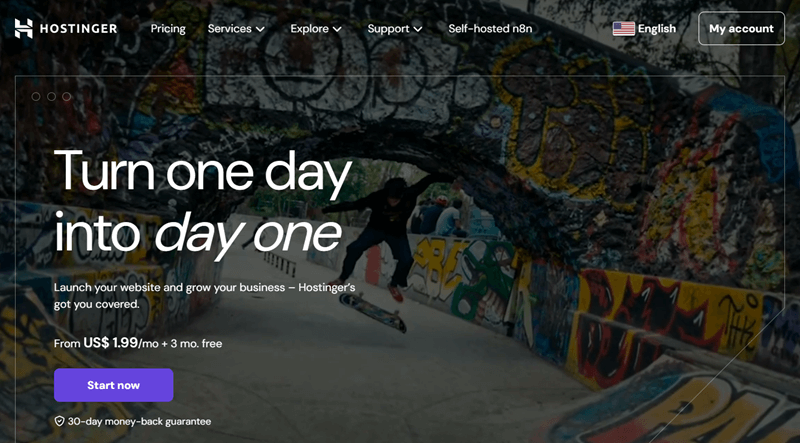
Once you’ve selected, simply click on the ‘Choose Plan’ option of the respective chosen plan.
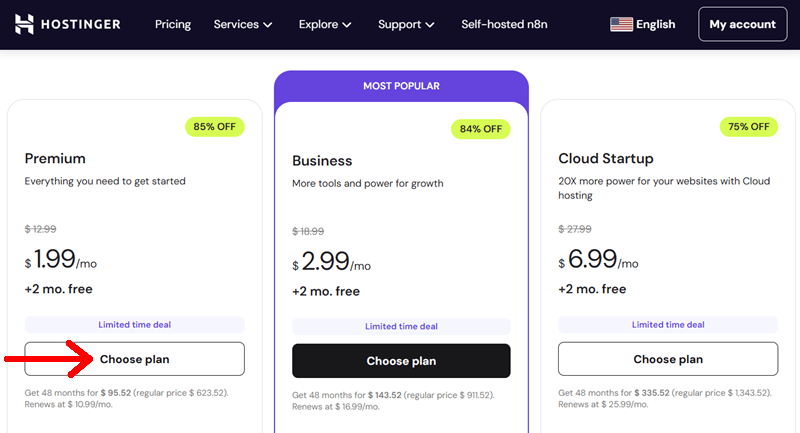
Next, you need to choose the duration (1 month, 12 months, 24 months, or 48 months for the best discounts). For now, here we’ve chosen 1 month.
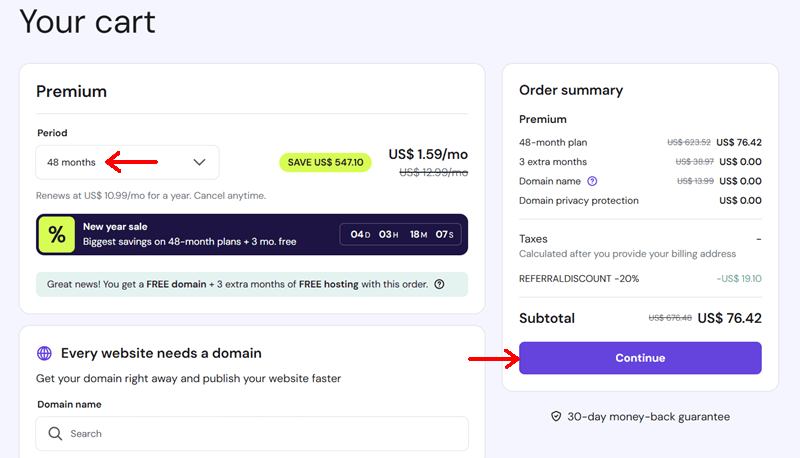
Then, click on the ‘Continue’ option to proceed to checkout.
Next, you need to create an account or log in, select your preferred payment method, and complete the purchase.
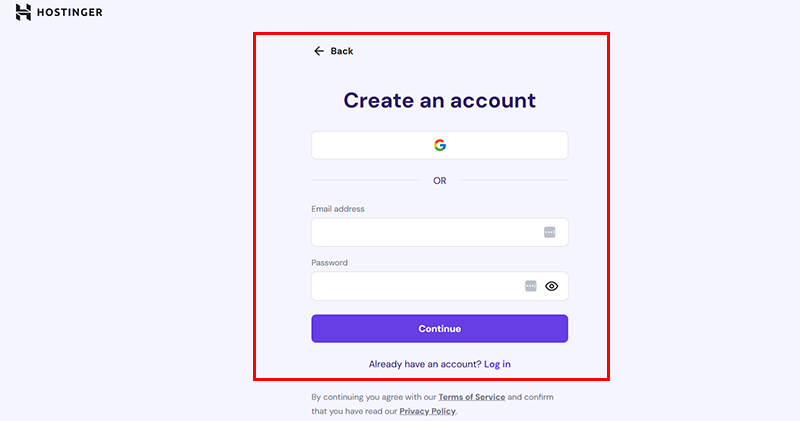
After payment, log in to hPanel (Hostinger’s control panel) to manage your hosting.
Last but not least, you need to connect your Namecheap domain to Hostinger and proceed forward. You can check this Namecheap’s documentation on how to connect a Namecheap domain to Hostinger for detailed guidance.
ii) How to Buy Domain & Hosting Together?
You can see some domain name registrars offering hosting services. Similarly, hosting companies have also been providing domain name registration.
So, you can purchase the domain and hosting both from a single platform if you like. It’s the best option if you’re a beginner.
Some of the platforms that provide both domain and web hosting from one place are Hostinger, Bluehost, etc.
If you want to buy a domain and hosting together, the process is much simpler since the domain is automatically linked to your hosting.
Here’s how you can do it via Hostinger:
Step 1: Choose a Hosting Plan
Like earlier, go to Hostinger and select a hosting plan that suits your needs.
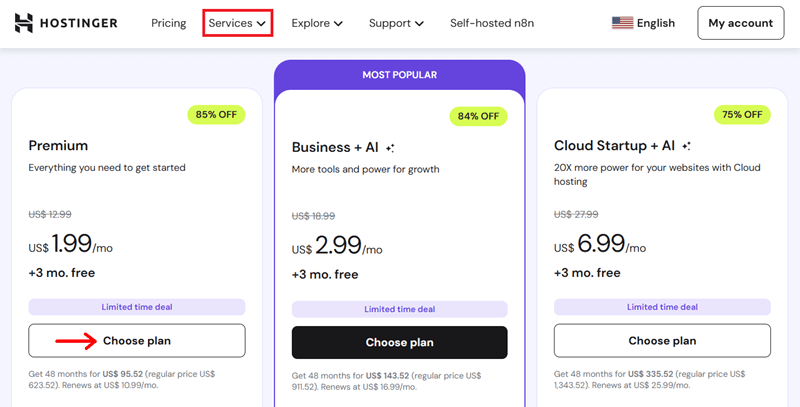
Once you’ve selected, simply click on the ‘Choose Plan’ option of the respective chosen plan.
Step 2: Select a Free or Custom Domain
Next, you need to choose the duration (1 month, 12 months, 24 months, or 48 months for the best discounts).
But before that, you need to enter your desired domain name and check availability. For example, here we’ve entered ‘sandyen.com‘, If it’s available, select it and proceed.
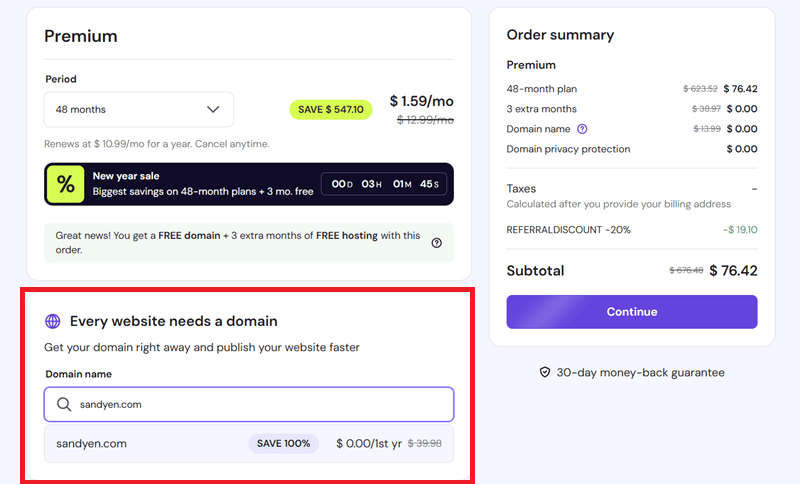
Step 3: Complete the Purchase
On top, here we’ve chosen 12 month since the free domain is available only in 1 year plan and onwards.
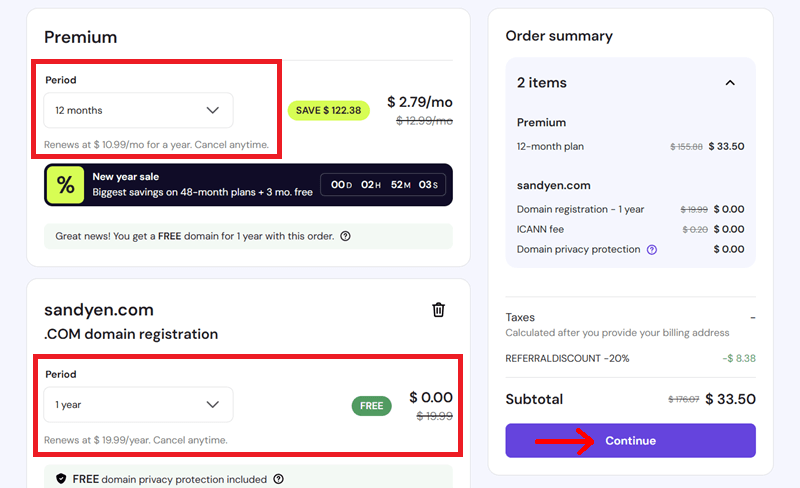
Then, click on the ‘Continue’ option to proceed to checkout.
Next, you need to create an account or log in, select your preferred payment method, and complete the purchase.

After purchase, Hostinger will automatically connect your domain to your hosting. This method is indeed quite cool, right?
Besides, if you’re looking for an alternative to Hostinger, then you can also opt for Bluehost which also provides both hosting and domain services in one-stop.
E. Frequently Asked Questions on Web Hosting vs Domain Name
Q.1 What is the main difference between web hosting and a domain name?
A domain name is the address of your website (e.g., www.example.com). While web hosting is the service that stores your website’s files and makes them accessible on the internet.
Think of it like this: the domain name is your home’s address, and web hosting is the actual house where your website’s content lives.
Q.2 Can I have a website without a domain name?
Technically, yes. You can access a website through its IP address, but this is not user-friendly. A domain name makes it easier for users to find and remember your site.
Q.3 Can I have a domain name without web hosting?
Yes, you can register a domain name without buying hosting. Many people do this to secure a name for future use or for email services. However, to launch a website, you will need web hosting.
Q.4 Do I need to buy domain and hosting from the same provider?
Q.5 What happens if my domain name expires?
If your domain expires, your website will become inaccessible. Most registrars offer a grace period where you can renew it, but after a certain period, it may be released and available for others to purchase.
Conclusion
That’s all, folks!
We hope you now clearly understand the differences between domain name and web hosting. We hope you like it too.
If you have suggestions, feedback, and want any help, then add your comments below.
You may like our article on the best domain name generators to find a good domain name.
Also, browse our article on how to choose a domain name for business and how to choose the domain name for affiliate marketing.
Lastly, stay connected with us on Facebook and X (Formerly Twitter) to stay updated with our upcoming articles.